Fluconazole powder is a broad-spectrum antifungal medication widely used in the treatment of various fungal infections. This versatile pharmaceutical compound belongs to the class of triazole antifungals and is available in both oral and intravenous formulations. Fluconazole powder is highly effective against a range of fungal pathogens, including Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, and various species of Aspergillus, making it a valuable tool in the medical arsenal against fungal diseases.
What is fluconazole powder used for?
Fluconazole powder is a potent antifungal agent with a wide range of applications in the treatment of various fungal infections. One of its primary uses is in the management of candidiasis, a fungal infection caused by the Candida species. Candidiasis can manifest in various forms, including vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, and invasive candidiasis affecting the bloodstream or internal organs. Fluconazole powder is highly effective in combating these infections, providing relief from symptoms and preventing further complications.
Another significant application of fluconazole powder is in the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis, a serious fungal infection of the brain and spinal cord caused by the Cryptococcus neoformans fungus. This condition is particularly prevalent in individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those living with HIV/AIDS or receiving immunosuppressive therapy. Fluconazole powder has proven to be a valuable treatment option for cryptococcal meningitis, helping to alleviate symptoms and prevent potential neurological damage.
Fluconazole powder is also widely used in the prophylaxis (prevention) of fungal infections in high-risk patients. This includes individuals undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplantation, as well as those with weakened immune systems due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or prolonged corticosteroid use. By administering fluconazole powder prophylactically, healthcare professionals can reduce the risk of opportunistic fungal infections in these vulnerable populations.
How does fluconazole powder work?
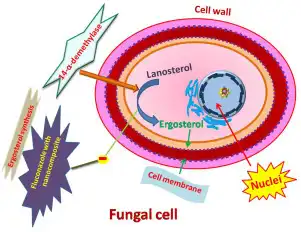
Fluconazole powder exerts its antifungal effects by inhibiting the biosynthesis of ergosterol, a vital component of the fungal cell membrane. Ergosterol plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity and fluidity of the fungal cell membrane, similar to the function of cholesterol in human cell membranes.
The mechanism of action of fluconazole powder involves binding to and inhibiting the enzyme lanosterol 14α-demethylase, which is responsible for a critical step in the biosynthesis of ergosterol. By disrupting this process, fluconazole powder impairs the ability of the fungal cell to produce ergosterol, leading to the formation of defective cell membranes.
Consequently, the fungal cell membranes become more permeable, allowing essential cellular components to leak out and ultimately leading to the death of the fungal cell. This mode of action makes fluconazole powder effective against a wide range of fungal species, as ergosterol biosynthesis is a conserved process across various fungal pathogens.
In addition to its antifungal properties, fluconazole powder also exhibits anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects, which may contribute to its therapeutic efficacy in certain fungal infections. However, the exact mechanisms underlying these additional effects are not fully understood and require further research.
What are the side effects of fluconazole powder?
Like any medication, fluconazole powder can potentially cause side effects, although the risk and severity of these adverse effects vary from person to person. Some of the most commonly reported side effects associated with fluconazole powder include:
1. Gastrointestinal disturbances: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite are among the gastrointestinal side effects that may occur during fluconazole therapy.
2. Headaches: Some individuals may experience headaches or migraines while taking fluconazole powder.
3. Rash or skin reactions: Fluconazole can cause skin rashes, itching, or other dermatological reactions in some patients.
4. Liver enzyme elevation: Fluconazole has been associated with increased levels of liver enzymes, particularly in patients receiving high doses or prolonged treatment. Regular monitoring of liver function is recommended during fluconazole therapy.
5. Allergic reactions: Although rare, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to fluconazole, ranging from mild symptoms like hives or rashes to severe anaphylactic reactions.
6. Drug interactions: Fluconazole can interact with certain medications, altering their metabolism and potentially increasing or decreasing their effectiveness. Patients should inform their healthcare providers about any other medications they are taking to avoid potential interactions.
It is important to note that most side effects associated with fluconazole powder are generally mild and resolve upon discontinuation of the medication. However, if severe or persistent side effects occur, it is advisable to seek medical attention promptly.
Conclusion
Fluconazole powder is a highly effective and widely used antifungal medication that has revolutionized the treatment of various fungal infections. Its broad-spectrum activity, coupled with its excellent safety profile, has made it a valuable asset in the medical community. However, as with any medication, it is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and consult with healthcare professionals to ensure proper monitoring and management of potential side effects. With responsible use and appropriate precautions, fluconazole powder continues to play a vital role in combating fungal diseases and improving patient outcomes.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact iceyqiang@gmail.com.
References:
1. Pappas, P. G., Kauffman, C. A., Andes, D. R., Clancy, C. J., Marr, K. A., Ostrosky-Zeichner, L., ... & Sobel, J. D. (2016). Clinical practice guideline for the management of candidiasis: 2016 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 62(4), e1-e50.
2. Dismukes, W. E., Cloud, G., Gallis, H. A., Kerkering, T. M., Medoff, G., Craven, P. C., ... & Graybill, J. R. (1987). Treatment of cryptococcal meningitis with combination amphotericin B and fluconazole for four as outpatient therapy. New England Journal of Medicine, 317(6), 334-338.
3. Sipsas, N. V., & Kontoyiannis, D. P. (2012). Invasive fungal infections in patients with cancer in the Intensive Care Unit. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 39(6), 464-471.
4. Girmenia, C., Finolezzi, E., Federico, V., Santopietro, M., Perrone, S., Marenco, G., ... & Martino, P. (2005). Invasive fungal infections during first induction chemotherapy in patients with acute leukemia. Annals of hematology, 84(7), 437-443.
5. Odds, F. C., Brown, A. J., & Gow, N. A. (2003). Antifungal agents: mechanisms of action. Trends in microbiology, 11(6), 272-279.
6. Vazquez, J. A., & Sobel, J. D. (2002). Mucosal candidiasis. Infectious Disease Clinics, 16(4), 793-820.
7. Charlier, C., Hart, E., Lefort, A., Clumeck, N., Wouters, C., Mikulska, M., ... & Aoun, M. (2006). Fluconazole for the management of invasive candidiasis: where do we stand after 15 years?. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 57(3), 384-410.
8. Panackal, A. A., & Wuest, S. C. (2022). Fluconazole. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
9. Dunkle, L. M., Furr, M. O., & Kunze, S. (1991). Fluconazole for the prevention of fungal infections in immunocompromised patients. American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy, 48(9), 1903-1909.
10. Debruyne, D., & Coquerel, A. (2001). Pharmacokinetics of antifungal agents in oncology.







