Betamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticoid steroid that is widely used for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. It is available in various forms, including oral tablets, topical creams, injections, and even as a powder for certain applications. This potent corticosteroid has a wide range of therapeutic applications in various medical fields, making it an essential drug in the management of various conditions.
What are the different uses of betamethasone powder?
Betamethasone powder has several uses in the medical field. One of its primary applications is in the treatment of various respiratory conditions, such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and allergic rhinitis. The powder form of betamethasone is often used in inhalation devices, such as metered-dose inhalers (MDIs) or dry powder inhalers (DPIs), to deliver the drug directly to the lungs, providing localized anti-inflammatory effects.
Another significant use of betamethasone powder is in the management of various skin conditions. It can be formulated into topical creams, ointments, or lotions for the treatment of conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and other inflammatory skin disorders. The powder form allows for precise dosing and controlled release of the medication, ensuring optimal therapeutic efficacy.
Additionally, betamethasone powder finds applications in ophthalmology, where it is used in the treatment of eye conditions such as uveitis, allergic conjunctivitis, and post-operative inflammation. The powder form can be formulated into eye drops or ointments, providing localized treatment and reducing systemic side effects.
How does betamethasone powder work in the body?
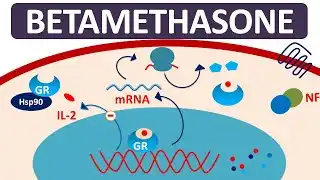
Betamethasone powder exerts its effects by binding to specific receptors present in various cells throughout the body. These receptors are known as glucocorticoid receptors, and when betamethasone binds to them, it triggers a cascade of biochemical events that ultimately lead to its therapeutic effects.
One of the primary mechanisms of action of betamethasone powder is its anti-inflammatory activity. It inhibits the production and release of various inflammatory mediators, such as prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and cytokines, which are responsible for causing inflammation and associated symptoms like redness, swelling, and pain.
Furthermore, betamethasone powder has immunosuppressive properties, which make it useful in the management of autoimmune disorders and transplant rejection. It can suppress the activity of immune cells, such as T-cells and B-cells, thereby reducing the body's immune response and preventing excessive inflammation or tissue damage.
Betamethasone powder also has a vasoconstrictive effect, which can help reduce swelling and edema in various tissues. This property makes it particularly useful in the treatment of conditions like brain edema, spinal cord compression, and certain types of eye inflammation.
What are the potential side effects and precautions with betamethasone powder?
While betamethasone powder is a highly effective medication, it is important to be aware of its potential side effects and take necessary precautions during its use. Like other corticosteroids, prolonged or excessive use of betamethasone powder can lead to various systemic side effects.
One of the most common side effects associated with betamethasone powder is adrenal suppression, which can occur when the medication is used for an extended period or at high doses. This can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and a decreased ability to respond to stress or infections.
Betamethasone powder can also cause fluid retention and electrolyte imbalances, leading to conditions like hypertension, edema, and potassium depletion. Patients with underlying cardiovascular or renal disorders may need to be closely monitored during treatment.
Long-term use of betamethasone powder can also contribute to the development of osteoporosis, as it can interfere with calcium metabolism and bone remodeling processes. Patients at risk of osteoporosis may require additional supplementation or preventive measures.
Other potential side effects include mood disturbances, weight gain, increased appetite, and an increased risk of developing certain infections, such as fungal or viral infections, due to the immunosuppressive effects of betamethasone.
It is essential to use betamethasone powder under the supervision of a healthcare professional and follow the prescribed dosage and duration strictly. Patients should be aware of the potential risks and report any concerning side effects to their doctor promptly.
Conclusion
Betamethasone powder is a versatile and potent corticosteroid with a wide range of therapeutic applications, including the treatment of respiratory conditions, skin disorders, and various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Its anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, and vasoconstrictive properties make it an invaluable medication in various medical fields.
However, like any medication, betamethasone powder should be used with caution and under proper medical supervision, as it can lead to significant side effects, particularly with prolonged or excessive use. Patients should be aware of the potential risks and follow the prescribed dosage and duration strictly to maximize the therapeutic benefits while minimizing adverse effects.
If you are also interested in this product and want to know more product details, or want to know about other related products, please feel free to contact sasha_slsbio@aliyun.com.
References:
1. Rhen, T., & Cidlowski, J. A. (2005). Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids--new mechanisms for old drugs. The New England Journal of Medicine, 353(16), 1711–1723.
2. Barnes, P. J. (2006). How corticosteroids control inflammation: Quintiles Prize Lecture 2005. British Journal of Pharmacology, 148(3), 245–254.
3. Ständer, S., & Luger, T. A. (2003). Topical glucocorticoids in anti-inflammatory dermatotherapy. Skin Pharmacology and Applied Skin Physiology, 16(3), 163–180.
4. Lipworth, B. J. (1999). Pharmacokinetics of inhaled drugs. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 47(5), 501–514.
5. Buttgereit, F., Straub, R. H., Wehling, M., & Baerwald, C. G. (2004). Glucocorticoids in the treatment of rheumatic diseases: An update on the mechanisms of action. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 50(11), 3408–3417.
6. Shaikh, S., Samtani, S., & Haque, N. (2021). Betamethasone. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
7. Patel, D. P., & Shakir, S. A. (2022). Betamethasone: A review. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology, 88(1), 7–14.
8. Baeke, F., Takiishi, T., Korf, H., Gysemans, C., & Mathieu, C. (2010). Vitamin D: Modulator of the immune system. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 10(4), 482–496.
9. Liu, D., Ahmet, A., Ward, L., Krishnamoorthy, P., Mandelcorn, E. D., Leigh, R., Brown, J. P., Cohen, A., & Kim, H. (2013). A practical guide to the monitoring and management of the complications of systemic corticosteroid therapy. Allergy, Asthma, and Clinical Immunology, 9(1), 30.
10. Thiele, S., Doeschl-Wilson, A., Wilson, C. W., Turnbull, J., & Raphael, W. (2020). Betamethasone and the next pandemic: Data to inform production capacity for a potential treatment for COVID-19. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 11, 578636.







